

The below output clearly shows that 'RAID 1' is configured on the 'cciss0' array controller. You can identify the device name using the df command as shown below: df -h | grep cciss To view the configuration of each controller, use the following command.
RAID MONITOR LINUX DRIVER
lspci | grep -i raidĠc:00.0 RAID bus controller: Hewlett-Packard Company Smart Array G6 controllers (rev 01)Ĭciss is a block driver for older HP Smart Array RAID controllers. The below output shows the raid controller is present on the system, which doesn’t mean that we have already configured RAID on the server.
Use the lspci command to check if your system has physical RAID controller or not, in most cases physical servers use to have hardware raid controller.
RAID MONITOR LINUX HOW TO
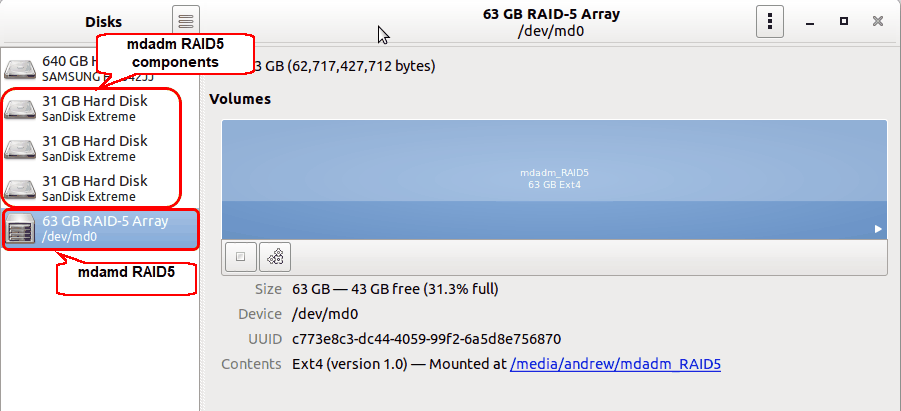
How to Check Hardware RAID Configuration on HP ProLiant Servers In this guide, we’ll show you how to check hardware RAID configured on HP ProLiant servers from Linux. It combines multiple physical hard disk drives into one or more logical drive to improve performance and reliability. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks. It means, it does not take any resources from the operating system to perform raid related tasks. The RAID controller manages and performs all RAID-related tasks independently of the OS. But in RAID 5 we should have at least 3 storage devices.Hardware RAID is configured on the physical servers, which use a dedicated RAID controller to manage the raid configuration. When in a damaged state, RAID 5 will suffer from very poor results.įor creating the RAID 5 array, we have to first identify the component devices as we identified in RAID 0. While the info about parity is shared, the storage value of one disc can be used for parity. The system obtaining the parity block is rotated such that there is a balanced sum of parity information for each device. The parity block and the remaining blocks will be used to determine the missing data in case the device fails. A measured parity block is one part of each stripe. Raid 5 arrays are created by stripping the data along with various devices. In order to mount automatically at boot, add new file system mount options in etc/fstab file available:Įach boot can now automatically add your RAID 0 array and mount it. :~$ sudo mdadm -detail -scan | sudo tee -a /etc /mdadm /nf In order to get started, you have to first identify the component devices by using the following command: In raid 0, as blocks are striped, its performance is excellent, but due to no mirroring strategy, a single failure of the device would destroy all the data. Means that each disc holds a portion of the data and while accessing that data, several discs would be referenced. RAID 0 is the mechanism by which data is separated into blocks, and those blocks are scattered through various storage devices like hard drives. Let’s look at creating different kinds of Raid arrays using mdadm. The name derives from the nodes of the multiple devices (md) that it controls or manages.
Several core operating modes of mdadm are assembled, build, create, follow, monitor, grow, incremental and auto-detect. Mdadm is a Linux utility used to control and manage RAID devices for applications.

RAID MONITOR LINUX SOFTWARE
The Linux software RAID array currently supports RAID 0 (strip), RAID 1 (mirror), RAID 4, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10. The RAID devices are deployed via the application driver md. RAID levels higher than RAID 0 offer protection against unrepairable read errors in the field, as well as against entire physical drive failures. The storage capacity of each drive is split into units that range from a sector (512 bytes) up to multiple megabytes. Partition striping allows distributing data across many disc drives. RAID uses disc mirroring or disc striping methods, mirroring on more than one drive would copy similar data. stability, usability, performance, and strength. Each system, or level of RAID, provides a different balance between the key goals, i.e. Different systems are known as ‘RAID’ followed by an integer, such as RAID 0 or RAID 1. Based on the required level of reliability and efficiency, data is scattered across the drives in one of many ways, referred to as RAID levels. RAID is a virtualization platform for data storage that integrates several physical disc drives into one or more logical units.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
